Theme: Biopharmaceutical Innovations: Ensuring Quality in Biosimilar Production
Eurobiosimilars 2024
Dear Esteemed Participants,
On behalf of the organizing committee, it is with great pleasure that I welcome you to the Euro Biosimilars 2024 conference, which will take place in the vibrant city of Madrid, Spain, on April 04-05, 2024.
This conference promises to be a premier platform for professionals, researchers, and experts in the field of biosimilars to exchange ideas, share knowledge, and collaborate on the latest developments in this rapidly evolving industry. With a lineup of renowned speakers, insightful presentations, and interactive sessions, Euro Biosimilars 2024 is poised to be an enlightening experience for all attendees.
Madrid, a city renowned for its rich history, culture, and innovation, provides the perfect backdrop for this conference. The historic charm and modern vibrancy of the city will undoubtedly enhance your experience and create an inspiring environment for networking and learning.
We look forward to your active participation, valuable contributions, and the opportunity to forge new connections with your peers. Let's come together to explore the future of biosimilars and drive innovation in the healthcare sector.
Thank you for being a part of Euro Biosimilars 2024. We wish you a productive and enjoyable conference!
With 10 years now added to its repertoire, European Biosimilars Congress is really turning into a staple meeting where Biosimilars partners accumulate to address the present and future condition of Biosimilars in the Europe.
The addition of two dedicated streams at the European Biosimilars Congress meeting proved to be highly successful, providing valuable insights from two distinct groups. One group excelled in the scientific and technical aspects, offering in-depth knowledge and expertise in research and manufacturing. The other group excelled in the business and strategic aspects, providing valuable insights into market trends, commercialization strategies, and regulatory considerations. This dual-stream approach allowed participants to gain a comprehensive understanding of both the scientific and commercial aspects of the biosimilars industry. The positive response and knowledge exchange from these two specialized streams contributed to the overall success of the European Biosimilars Congress meeting.
The 2024 establishment of this meeting will enable us to keep on diving further into both the investigation of Biosimilars improvement – and the business requirements for organizations that keep on seeking FDA endorsement.
The Organizing Committee is delighted to invite you to attend the Euro Biosimilars one of its remarkable Pharmaceutical conferences, to be held during April 04-05, 2024 at Madrid, Spain. European Biosimilars Congress is a global annual event. This European Biosimilars Congress 2024 will bring together scientists, researchers, business development managers, CEOs, directors, IP Attorneys, Regulatory Officials and CROs from around the world. Many biologics products are making their entry in the pharma market and experiencing a notable rise in their usage over the conventional medications.
At Euro Bisimilars 2024 meet your target audiences from around the world focused on learning about biologics and Biosimilars. This conference would be your single best opportunity to reach the largest assemblage of participants from the biologics and Biosimilars community.
2024 Highlights:
- 300+ Participation (70 Industry: 30 Academia)
- 10+ Keynote Speakers
- 50+ Plenary Speakers
- 20+ Exhibitors
- 14 Innovative Educational Sessions
- 5+ Workshops
- B2B Meetings
Euro Biosimilars 2024 has everything you need:
Open panel discussions: Providing an open forum with experts from academia and business to discuss on current challenges in Biosimilars & Biologics, where all attendees can interact with the panel followed by a Q&A session.
Speaker and poster presentations: Providing a platform to all academicians and industry professionals to share their research thoughts and findings through a speech or a poster presentation.
Editorial board meeting: Discussing on growth and development of open access Bioanalysis and Biomedicine International Journals and recruiting board members and reviewers who can support the journal.
Round table meetings: Providing a platform where industry professionals meet academic experts.
The Euro Biosimilars 2024 conference will host a diverse range of exhibitors, with over 50+ organizations and international pavilions participating. The exhibition will feature a wide array of industry stakeholders, including equipment manufacturers, suppliers, systems providers, finance and investment firms, R&D companies, project developers, trade associations, and government agencies. This diverse representation underscores the significance and breadth of the biosimilars sector. Attendees can expect to engage with leading companies and institutions from various sectors, fostering collaborations, knowledge exchange, and advancements in the field of biosimilars.
In addition to the products and services you will have access to valuable content, including Keynote Presentations, Product Demonstrations and Educational Sessions from today’s industry leaders.
The Euro Biosimilars 2024 has everything you need, all under one roof, saving you both time and money. It is the event you cannot afford to miss!
Target Audience:
- Directors, CEO’s of Organizations
- Business Development Managers
- Chief Scientific Officers
- R&D Researchers from Biosimilar and Bioslogics Industries
- Professors, Associate Professors, Assistant Professors
- PhD Scholars
- Patent Attorneys
- Intellectual Property Attorneys
- Investment Analysts
- Association, Association presidents and professionals
- Noble laureates in Health Care and Medicine
- Bio instruments Professionals
- Bio-informatics Professionals
- Software development companies
- Research Institutes and members
- Supply Chain companies
- Manufacturing Companies
- CRO and DATA management Companies
- Training Institutes
- Business Entrepreneurs
Track 1: Current Challenges in Developing Biosimilars
The development of biosimilars presents a myriad of current challenges. One major hurdle is the complex nature of biologic drugs, which are derived from living organisms and exhibit intricate structures and functions. Replicating these characteristics with high accuracy requires extensive scientific knowledge and advanced technology. Additionally, regulatory requirements for biosimilars demand comprehensive data demonstrating similarity to the reference biologic, including rigorous comparability studies. This necessitates significant investment in research and development, as well as clinical trials to ensure safety and efficacy. Moreover, intellectual property considerations and legal frameworks pose additional obstacles for biosimilar manufacturers. Overcoming these challenges requires collaboration between scientific experts, regulatory authorities, and industry stakeholders to foster a robust biosimilar development ecosystem.
Track 2: Chemical and Analytical Strategies for Biosimilars
Chemical and analytical strategies play a vital role in the development and characterization of biosimilars. These strategies aim to establish comparability between the biosimilar and the reference biologic by assessing their physicochemical properties, purity, and potency. Various analytical techniques, such as mass spectrometry, chromatography, and spectroscopy, are employed to evaluate critical quality attributes (CQAs) of the biosimilar. Additionally, advanced structural analysis techniques, including X-ray crystallography and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy, are used to examine the higher-order structure of the biosimilar. These strategies enable a comprehensive understanding of the biosimilar's molecular characteristics, facilitating the identification of potential differences and ensuring the safety and efficacy of the product.
Track 3: Intellectual Property Rights
Intellectual property rights (IPR) refer to legal rights granted to individuals or organizations to protect their creations or inventions. These rights provide exclusive ownership and control over intangible assets, including patents, trademarks, copyrights, and trade secrets. Intellectual property serves as an incentive for innovation by granting creators and inventors the ability to monetize their work and prevent unauthorized use or reproduction by others. It encourages research and development, fosters economic growth, and promotes creativity in various industries. However, managing intellectual property can be complex, as it involves navigating legal frameworks, enforcing rights, and addressing infringement issues. Striking a balance between protecting intellectual property and promoting access to knowledge remains a challenge, particularly in areas such as technology, pharmaceuticals, and entertainment, where rapid advancements and evolving business models constantly reshape the IPR landscape.
Track 4: Biological Medicine
Biological medicine, also known as biologics, refers to therapeutic products derived from living organisms or their components. Unlike traditional chemical-based drugs, biological medicines are typically large and complex molecules, including proteins, antibodies, and nucleic acids. These medicines are designed to target specific disease mechanisms, offering innovative treatment options for various diseases such as cancer, autoimmune disorders, and chronic illnesses. Biological medicines are produced using advanced biotechnological processes, such as genetic engineering and cell culture techniques. Due to their complexity and manufacturing intricacies, the development, production, and regulation of biological medicines require specialized expertise and stringent quality control measures. Despite the challenges, biological medicine continues to revolutionize healthcare by providing targeted and personalized therapies that have the potential to improve patient outcomes and quality of life.
Track 5: Emerging Biosimilars in Therapeutics
Emerging biosimilars in therapeutics are poised to revolutionize the healthcare landscape by expanding access to effective and more affordable treatment options. As patents for reference biologics expire, biosimilar versions are being developed and introduced into the market. These emerging biosimilars aim to demonstrate comparable safety, efficacy, and quality to their reference biologics through rigorous analytical and clinical evaluations. By offering cost-effective alternatives, biosimilars have the potential to improve patient access to life-saving treatments for diseases such as cancer, autoimmune disorders, and chronic conditions. Additionally, biosimilars stimulate competition in the biopharmaceutical industry, driving innovation and reducing healthcare costs. With continued research, development, and regulatory support, emerging biosimilars have the potential to transform patient care and enhance the sustainability of healthcare systems worldwide.
Track 6: Innovative Clinical Approach in Biosimilars
Innovative clinical approaches in biosimilars aim to streamline the development and evaluation process while ensuring patient safety and efficacy. Adaptive clinical trial designs, such as seamless phase transitions or Bayesian methods, allow for more efficient and flexible study protocols. These approaches optimize sample size, enhance statistical power, and enable real-time adjustments based on emerging data. Additionally, the use of biomarkers and predictive modeling helps identify patient populations likely to respond favorably to biosimilars, facilitating targeted treatment approaches. Furthermore, real-world evidence studies and post-marketing surveillance play a crucial role in monitoring the long-term safety and effectiveness of biosimilars. By embracing innovative clinical approaches, the development and adoption of biosimilars can be accelerated, benefiting patients and healthcare systems worldwide.
Track 7: Regulatory updates on Biosimilars
Regulatory updates on biosimilars play a vital role in ensuring patient safety, fostering competition, and promoting access to affordable biological therapies. Regulatory authorities, such as the FDA and EMA, continuously refine and update guidelines to provide clear pathways for the development, approval, and post-marketing surveillance of biosimilars. These updates often include guidance on demonstrating similarity, interchangeability, and extrapolation of indications. Additionally, regulatory agencies strive to enhance transparency and education for healthcare professionals and patients regarding biosimilar products. As the field of biosimilars evolves, regulatory updates address emerging challenges, such as interchangeability and naming conventions, to provide a robust framework for market entry and to inspire confidence in these cost-effective alternatives. Regular updates ensure that regulatory frameworks keep pace with scientific advancements and contribute to the continued growth and acceptance of biosimilars in clinical practice.
Track 8: Biosimilars Development in Markets
Biosimilars development in markets has gained significant traction, offering potential benefits in terms of cost savings, increased access to treatments, and fostering competition. As patents for reference biologics expire, biosimilar manufacturers seize the opportunity to enter the market with their comparable versions. However, successful market entry for biosimilars is dependent on several factors, including regulatory approval, pricing strategies, physician and patient acceptance, and reimbursement policies. Education and awareness campaigns are crucial to address misconceptions and build confidence in biosimilars among healthcare professionals and patients. Market dynamics vary across regions, with some markets being more receptive to biosimilars than others. As biosimilars continue to gain momentum, strategic partnerships, effective marketing, and robust supply chains will play a pivotal role in driving their adoption and market success.
Track 9: Biosimilars Approval to Biogenerics in Clinical Practice
The approval and integration of biosimilars, also known as biogenerics, into clinical practice have the potential to transform patient care by expanding treatment options and improving affordability. Regulatory agencies, such as the FDA and EMA, rigorously assess the comparability of biosimilars to their reference biologics through comprehensive scientific evaluations and clinical trials. Once approved, biosimilars are prescribed by healthcare professionals who consider factors such as safety, efficacy, and cost-effectiveness. Clinical practice guidelines and educational initiatives aid in the appropriate and informed use of biosimilars, ensuring patient safety and optimizing outcomes. As healthcare systems embrace biosimilars, their integration into clinical practice holds promise for reducing treatment costs, increasing patient access, and improving overall healthcare sustainability.
Track 10: Biopharmaceutical Informatics
Biopharmaceutical informatics, also known as bioinformatics in the context of pharmaceuticals, involves the application of computational and information science methods to collect, analyze, and interpret biological and pharmaceutical data. It encompasses a wide range of techniques and tools that aid in the discovery, development, and optimization of biopharmaceutical products. Biopharmaceutical informatics enables the efficient handling and integration of complex data sets, such as genomics, proteomics, and clinical trial data, to gain insights into disease mechanisms, target identification, and drug design. It also plays a crucial role in pharmacovigilance, drug safety assessment, and personalized medicine approaches. By leveraging computational models, machine learning algorithms, and data mining techniques, biopharmaceutical informatics accelerates research and development processes, facilitates decision-making, and supports evidence-based healthcare practices.
Track 11: Consequences of Brexit on Biosimilars
Brexit, the United Kingdom's withdrawal from the European Union (EU), has had several consequences on biosimilars. Prior to Brexit, the EU provided a unified regulatory framework for the approval and market access of biosimilars across member states. However, with the UK's departure, the Medicines and Healthcare products Regulatory Agency (MHRA) now oversees the regulation and approval of biosimilars specifically for the UK market. This has led to additional regulatory complexities and increased costs for biosimilar manufacturers who need to navigate separate approval processes for the UK and EU markets. Moreover, the divergence in regulations between the UK and the EU has resulted in uncertainties regarding mutual recognition and potential delays in launching biosimilars in both regions. These consequences have introduced challenges for biosimilar developers and impacted patient access to more affordable treatment options in both the UK and EU markets.
Track 12: BCS and IVIVC Based Biowaivers
Biopharmaceutics Classification System (BCS) and In Vitro-In Vivo Correlation (IVIVC) are important concepts in the pharmaceutical industry that can facilitate the approval process for generic drugs, including biowaivers for certain dosage forms. BCS categorizes drugs based on their solubility and permeability characteristics, allowing for predictions about their bioavailability. Drugs falling into BCS Class I and III, which are highly soluble and highly permeable, respectively, are often eligible for biowaivers. IVIVC is a scientific approach that establishes a relationship between in vitro dissolution profiles and in vivo drug absorption, helping to bridge the gap between lab testing and clinical outcomes. The utilization of BCS and IVIVC based biowaivers in drug development can save time and costs, enabling the faster introduction of generic and biosimilar products to the market, ultimately benefiting patients by increasing accessibility to affordable medications.
Track 13: Biosimilars Market and Cost Analysis
The biosimilars market and cost analysis are crucial aspects in evaluating the economic impact of biosimilar products. Biosimilars offer the potential for cost savings compared to their reference biologics, providing opportunities to reduce healthcare expenditure. Market analysis involves assessing factors such as market size, competition, and pricing strategies of biosimilar manufacturers. Cost analysis evaluates the pricing and cost-effectiveness of biosimilars in comparison to reference biologics, taking into account factors such as production costs, research and development investments, and market dynamics. By conducting comprehensive market and cost analyses, stakeholders, including healthcare providers, payers, and policymakers, can make informed decisions regarding the adoption and utilization of biosimilars, leading to improved affordability and accessibility of these important therapies.
Track 14: Challenges in Biosimilars Pharmacovigilance
Biosimilars pharmacovigilance presents unique challenges due to the complex nature of these products and the need for comprehensive monitoring of their safety profiles. One challenge is the potential for immunogenicity, as biosimilars can elicit immune responses in patients, leading to adverse reactions. Robust pharmacovigilance systems must be in place to detect and evaluate such events. Additionally, post-marketing surveillance for biosimilars requires effective traceability systems to distinguish between different products, ensuring accurate reporting and monitoring of adverse events. Furthermore, the global nature of biosimilar markets poses challenges in harmonizing pharmacovigilance practices and exchanging safety information across different regulatory authorities. Addressing these challenges necessitates close collaboration among stakeholders, standardized reporting frameworks, and ongoing vigilance to ensure the continued safety and confidence in biosimilars.
Track 15: Legal Issues and BPCI Act
Legal issues surrounding biosimilars revolve around intellectual property rights, patent disputes, and regulatory frameworks. The Biologics Price Competition and Innovation (BPCI) Act, enacted in the United States, created a pathway for the approval and market entry of biosimilars. However, legal challenges arise from patent litigation initiated by reference biologic manufacturers to protect their exclusivity. These disputes can delay the launch of biosimilars and extend market exclusivity for reference products. The BPCI Act also addresses the interchangeability of biosimilars, providing a framework for automatic substitution at the pharmacy level. However, state-specific laws and regulations can introduce further legal complexities. Navigating these legal issues requires a thorough understanding of intellectual property laws, regulatory guidelines, and litigation strategies to ensure fair market competition and patient access to affordable biosimilars.
Track 16: Formulation Strategies for Follow-on Biologics
Formulation strategies for follow-on biologics, also known as biosimilars, are essential for ensuring product stability, efficacy, and safety. These strategies focus on developing formulations that maintain the critical quality attributes (CQAs) of the reference biologic while optimizing manufacturing processes and minimizing variability. Formulation considerations include excipient selection, pH adjustment, buffer systems, and stabilization techniques to prevent protein degradation and maintain structural integrity. Additionally, advanced technologies such as protein engineering, controlled release systems, and drug delivery platforms can be employed to enhance the performance and patient experience of biosimilars. Formulation strategies play a crucial role in achieving bioequivalence between biosimilars and their reference products, ensuring consistent therapeutic outcomes and facilitating their successful development and commercialization.
Track 17: Current Agency Expectations for Approval for Biosimilars
Current agency expectations for the approval of biosimilars focus on demonstrating a high level of similarity to the reference biologic in terms of quality, safety, and efficacy. Regulatory authorities, such as the FDA and EMA, require comprehensive analytical and preclinical data to establish a robust scientific foundation for biosimilarity. This includes extensive physicochemical and biological characterization, comparative pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies, and non-clinical toxicity assessments. Clinical trials are also conducted to demonstrate similar clinical efficacy and safety profiles. In addition to comparative data, agencies emphasize the importance of a thorough risk management plan and post-marketing surveillance to ensure ongoing safety monitoring. By meeting these agency expectations, biosimilar manufacturers can obtain regulatory approval and provide patients with cost-effective alternatives to reference biologics while maintaining high standards of quality and safety.
Track 18: Biosimilars Research Pipeline
The biosimilars research pipeline is an active area of investigation, with numerous molecules undergoing development and evaluation. Researchers are focusing on expanding the range of therapeutic indications for biosimilars, targeting diseases such as cancer, autoimmune disorders, and inflammatory conditions. Additionally, efforts are underway to enhance the manufacturing processes, improve characterization techniques, and explore novel drug delivery systems for biosimilars. The research pipeline also encompasses the development of biosimilars for complex biologics, such as monoclonal antibodies and fusion proteins, requiring innovative approaches and technologies. As research progresses, the biosimilars research pipeline holds promise for introducing a wider array of cost-effective treatment options, increasing patient access to essential therapies, and promoting competition in the biopharmaceutical market.
Track 19: Globalization of Biosimilars
The globalization of biosimilars has gained momentum as these products continue to expand their presence in international markets. Increased harmonization of regulatory frameworks, such as the EMA in Europe and the FDA in the United States, has facilitated the development, approval, and cross-border acceptance of biosimilars. Moreover, collaborations between biosimilar manufacturers, contract research organizations, and global supply chains have enabled efficient production and distribution of these products worldwide. The globalization of biosimilars has significant implications for patient access to affordable treatments, fostering competition, and reducing healthcare costs on a global scale. However, challenges remain in terms of navigating varying regulatory landscapes, addressing local market dynamics, and ensuring robust pharmacovigilance practices. By overcoming these challenges, the globalization of biosimilars has the potential to transform healthcare by improving access to life-saving therapies and promoting sustainable healthcare systems globally.
Track 20: Drug Delivery and Development
Drug delivery and development play a crucial role in optimizing the efficacy, safety, and patient experience of pharmaceutical products. Advancements in drug delivery technologies, such as nanoparticle-based systems, targeted drug delivery, and sustained-release formulations, enable precise and controlled release of drugs at specific sites in the body. These technologies enhance therapeutic outcomes, minimize side effects, and improve patient adherence to treatment regimens. In drug development, formulation scientists employ various strategies to improve drug solubility, stability, and bioavailability. They also explore novel delivery routes, such as transdermal, inhalation, and implantable systems, to enhance drug absorption and patient convenience. By integrating innovative drug delivery approaches into the development process, pharmaceutical researchers strive to maximize the therapeutic potential of drugs and enhance patient care.
Track 21: Monoclonal Antibody Biosimilars
Monoclonal antibody (mAb) biosimilars are an important segment of the biosimilars market, offering more affordable alternatives to reference mAb therapies. Developing biosimilars for mAbs presents unique challenges due to their complex structures and intricate manufacturing processes. Extensive analytical characterization, including physicochemical and functional assessments, is crucial to establish similarity to the reference mAb. Comparative clinical studies are conducted to demonstrate similar efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity profiles. Regulatory agencies have specific guidelines for the development and approval of mAb biosimilars, ensuring a comprehensive evaluation of quality attributes. The availability of mAb biosimilars expands treatment options for patients, increases competition, and potentially reduces healthcare costs, while maintaining high standards of safety and effectiveness.
Track 22: USFDA Approved Biosimilars
The USFDA has been actively approving biosimilars to increase patient access to more affordable treatment options. Some notable USFDA-approved biosimilars include those for reference biologics such as adalimumab, infliximab, and trastuzumab. These biosimilars have undergone rigorous evaluations to demonstrate similarity in terms of safety, efficacy, and quality to their respective reference products. The USFDA's approval of these biosimilars provides healthcare providers and patients with alternatives that offer similar clinical benefits while potentially reducing healthcare costs. The expanding portfolio of USFDA-approved biosimilars signifies the growing acceptance and adoption of these products in the United States, contributing to increased competition and improved accessibility to critical biologic therapies.
Biosimilars: Global Markets
As per market researchers the global "Biosimilars Market by Product (Recombinant Non-Glycosylated Proteins (Insulin, rHGH, Interferon), Glycosylated (mAb, EPO), Peptides (Glucagon, Calcitonin)), Manufacturing Type (In-house, Contract), Disease (Oncology, Autoimmune) - Global Forecast to 2023", The biosimilars market is expected to reach USD 23.63 Billion by 2023 from USD 5.95 Billion in 2018, at a CAGR of 31.7%. Granulocyte colony-stimulating factors (G-CSFs) reached $379.3 million in 2013. This segment is expected to increase from $453.6 million in 2014 to $1.1 billion by 2019, a CAGR of 20.2% from 2014 to 2019.
Source: BCC Research
Importance & Scope:
The European-based pharmaceutical industry makes a major contribution to the Europe, not just in financial terms but also in terms of high-trait employment. Globally Pharma Market ranges from $870-$900 billion and in Europe $260-$280 billion.
A global biosimilars strategy:
Developed markets: Developed markets, with the exception of the United States, represent the greatest biosimilars presence today. Most biosimilars manufacturers have been and remain focused on the developed markets – whether it is for their historic and current opportunities (EU) or for their future market potential (United States, Japan). Dedicated regulatory pathways set the foundation for stringent, abbreviated approval processes which, in turn, have fed investor enthusiasm. Biosimilars adoption in developed markets has been primarily payer-driven, especially in European markets, given payers’ urgent, unmet need to contain public health care expenditures. Further market uptake has been slowed by prescribers’ skepticism and low patient awareness. Still, developed markets continue to have the highest number of biosimilars molecules in development – estimated at 29 in Europe, 19 in the United States and seven in Japan.
Emerging markets: In today’s emerging markets, biosimilars are still nascent, with little to no presence. However, in contrasting emerging markets with developed markets, the limited patient access to affordable biologics and the openness of physicians to low-cost therapies may offer potentially significant opportunities. Today, emerging markets represent a snippet of total world biologic sales in value, less than seven to eight percent (versus 48.6 percent in the United States).ix Treatment rates for flagship biologics are still low compared to developed markets, despite existing demand. For example, the treatment rate of MabThera® in Brazil is three times lower than in the UK and six times lower than in the US.x Additionally, a recent Kantor Health Survey found that 20 percent of emerging market autoimmune patients use a biologic, with the distribution of biologics varying from 29 percent in China to 12 percent in Russia and a mere 6 percent in Brazil.xi This may indicate the presence of large pockets of non-consumption, especially within the growing middle class.
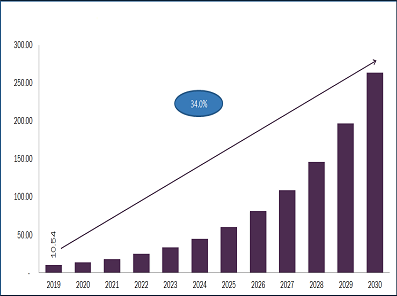
Biosimilars Market Projected To Reach $41.7 Billion By 2024
Biosimilars Market, by Product (Revenue, USD Million, 2017 - 2024)
-
Recombinant Non-Glycosylated Proteins
- Insulin
- Human Growth Hormones
- Granulocyte Colony-stimulating Factor (G-CSF)
- Interferons
-
Recombinant Glycosylated Proteins
- Erythropoietin
- Monoclonal Antibodies
- Follitropin
Biosimilars Market, by Application (Revenue, USD Million, 2017 - 2024)
- Oncology
- Blood Disorders
- Growth Hormone Deficiency
- Chronic and Autoimmune Disorders
- Others
Biosimilars Market, by Region (Revenue, USD Million, 2017 - 2024)
-
North America
- U.S.
- Canada
- Europe
- UK
- Germany
- China
- India
- Brazil
- Russia
- Asia Pacific
- Rest of the World
Analysis of selected countries:
United States
- FDA approval of the first biosimilar in March 2015 with Sandoz’s Zarxio (filgrastim)
- About 19 pipeline biosimilar molecules in development
- Represents about 50% of the global biologics market value and generates about 50% of the sales value growth
- Pending legislative decisions on data exclusivity period, naming conventions and interchangeability likely to have important implications.
Biosimilars approved in the US
In the US, a legal framework for approving biosimilars was established in 2009, via the Biologics Price Competition and Innovation Act of 2009 (BPCI Act).
The BPCI Act is part of the healthcare reform legislation, which was signed into law on 23 March 2010 by President Barack Obama. The BPCI Act establishes an abbreviated approval pathway for biological products that are demonstrated to be ‘highly similar’ (biosimilar) to, or ‘interchangeable’ with, a US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-licensed biological product.
FDA is still in the process of developing guidelines regarding these types of products and has issued several guidance documents on the subject.
Zarxio (filgrastim-sndz) was the first product approved in the US as a biosimilar in 2015. To date, FDA has approved four biosimilars within the product classes of anti-tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, and a follow-on biological in the product class of insulin for use in the US.
FDA approved Biosimilars and follow-on Biologicals
|
Product name |
Active substance |
Therapeutic area |
Authorization date |
Manufacturer/ Company name |
|
Amjevita (adalimumab-atto) |
adalimumab |
Ankylosing spondylitis |
23 Sep 2016 |
Amgen |
|
Basaglar# |
insulin glargine |
Diabetes |
16 Dec 2015 |
Eli Lilly/Boehringer Ingelheim |
|
Epoetin Hospira |
epoetin alfa |
Anaemia (chronic kidney disease, Zidovudine, chemotherapy) |
Recommended for approval by FDA’s Oncologic Drugs Advisory Committee (ODAC) on 25 May 2017 |
Pfizer (Hospira) |
|
Erelzi (etanercept-szzs) |
etanercept |
Axial spondyloarthritis |
30 Aug 2016 |
Sandoz |
|
Inflectra |
infliximab |
Ankylosing spondylitis |
5 Apr 2016 |
Pfizer (Hospira) |
|
Renflexis (infliximab-abda) |
infliximab |
Ankylosing spondylitis |
21 Apr 2017 |
Samsung Bioepis |
|
Zarxio |
filgrastim |
Autologous peripheral blood progenitor cell collection and therapy |
6 Mar 2015 |
Sandoz |
|
*Data collected on 30 September 2016, updated 26 June 2017 Source: US FDA |
||||
EU5
- Most mature biosimilar market representing 80% of global biosimilar spending
- Performance to date viewed as “disappointing” by select manufacturers
- Nineteen biosimilar products authorized in four molecule classes: human growth hormone, erythropoietin, G-CSF and tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-inhibitor
- About 29 pipeline biosimilars molecules in development.
- World-class dedicated pathway leaving questions of substitutability at the pharmacy level to member states
- Payer-driven uptake
- Challenged by continued pressure from strict regulatory decisions, lingering fear from prescribers around biosimilars’ “similarity”, safety and efficacy, debates on automatic substitution and INN prescription.
Biosimilars approved in Europe
In the European Union (EU), a legal framework for approving biosimilars was established in 2003. This framework means that biosimilars can only be approved centrally via the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and not nationally.
EMA first developed guidelines for the approval of biosimilars via an abbreviated registration process during 2005 to 2006, and since then EMA has developed many general and specific guidelines for biosimilars .
Omnitrope (somatropin) was the first product approved in the EU as a biosimilar in 2006. To date, EMA has approved 38 biosimilars within the product classes of human growth hormone, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, erythropoesis stimulating agent, insulin, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), parathyroid hormone and tumour necrosis factor (TNF)-inhibitor, for use in the EU. Three biosimilar approvals have been withdrawn; two for filgrastim biosimilars: Filgrastim ratiopharm in April 2011 and Biograstim in December 2016, and one for a somatropin biosimilar (Valtropin) in May 2012. This leaves a total of 35 biosimilars approved for use in Europe.
Conference Highlights
- Current Challenges in Developing Biosimilars
- Chemical and Analytical Strategies for Biosimilars
- Intellectual Property Rights
- Biological Medicine
- Emerging Biosimilars in Therapeutics
- Innovative Clinical Approach in Biosimilars
- Regulatory updates on Biosimilars
- Biosimilars Development in Markets
- Biosimilars Approval to Biogenerics in Clinical Practice
- Biopharmaceutical Informatics
- Consequences of Brexit on Biosimilars
- BCS and IVIVC Based Biowaivers
- Biosimilars Market and Cost Analysis
- Challenges in Biosimilars Pharmacovigilance
- Legal Issues and BPCI Act
- Formulation Strategies for Follow-on Biologics
- Current Agency Expectations for Approval for Biosimilars
- Biosimilars Research Pipeline
- Globalization of Biosimilars
- Drug Delivery and Development
- Monoclonal Antibody Biosimilars
- USFDA Approved Biosimilars
- Biosimilars and Cancer
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | April 04-05, 2024 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | Day 1 | ||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Bioanalysis & Biomedicine
- Journal of Pharmaceutical Bioprocessing
- Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences & Emerging Drugs
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by



















































